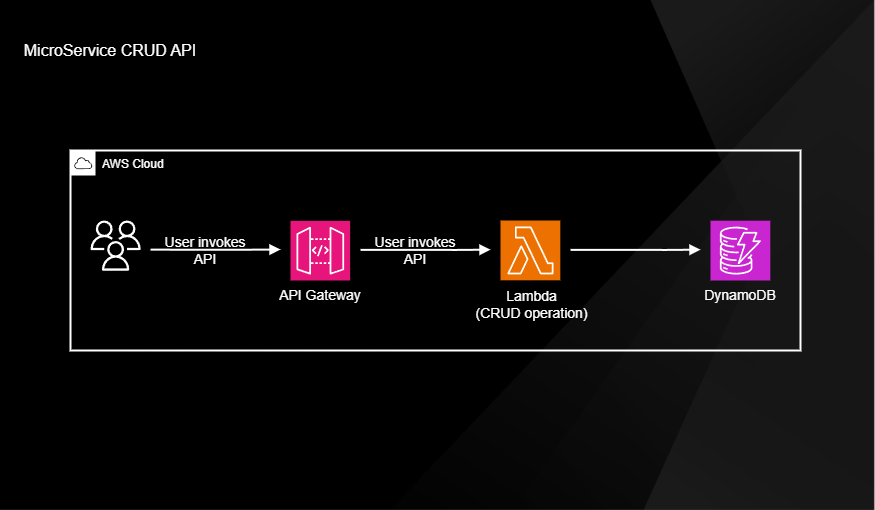
1. Project description
In this project I am creating a serverless RESTful API for CRUD operations for a DynamoDB. Creating an API Gateway with Lambda execution to create a RESTful API for DynamoDB offers several advantages and is a common architecture choice for building serverless and scalable web APIs.
- Scalability and Resilience: Lambda and API Gateway are managed services provided by AWS. They automatically scale to handle varying levels of traffic and are highly available and fault-tolerant. This means your API can handle spikes in traffic without you needing to manage server provisioning and scaling.
- No Server Management: With Lambda, you don't need to worry about server management, patching, or infrastructure scaling. You can focus solely on your code and business logic. This greatly reduces operational overhead.
- Cost-Effective: You pay only for the compute time used by your Lambda functions and the requests served by API Gateway. There are no idle servers, making it a cost-effective solution, especially for low to moderate traffic applications.
- Security: API Gateway provides features for securing your API, such as authentication and authorization. You can control access to your API, integrate with identity providers like Cognito, and use API keys for fine-grained control.
- RESTful Endpoints: API Gateway allows you to define RESTful endpoints, making it easy to design a clear and intuitive API structure that follows REST principles. This is especially useful when building APIs that are intended to be consumed by other developers.
- Caching: API Gateway supports caching, which can significantly reduce the load on your backend and improve response times for frequently requested data.
- Logging and Monitoring: AWS provides built-in logging and monitoring tools for both Lambda and API Gateway. You can monitor request/response metrics, set up alarms, and troubleshoot issues more easily.
- Integration with Other AWS Services: Lambda can be easily integrated with other AWS services like DynamoDB, S3, and more. This allows you to build powerful and flexible APIs that interact with various AWS resources.
- Versioning and Deployment: API Gateway supports versioning and allows you to deploy different versions of your API, making it easier to manage changes and updates without disrupting existing clients.
1.1 Technologies:
- DynamoDB
- API Gateway
- Lambda function
2. Create DynamoDB table
- Table name: DynDb-table1.
- Primary key: id (string).
- Settings: Default.
3. Create Lambda Function with permission
We need an IAM role with permission (for DynamoDB & CW logs) and attach it to the Lambda function in order to perform the operations.
3.1 Create Lambda IAM Role.
- Role name: lambda-apigateway-role.
-
Permissions: Custom policy with permission to DynamoDB and CloudWatch Logs.
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "VisualEditor0", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "logs:CreateLogStream", "dynamodb:PutItem", "dynamodb:DeleteItem", "dynamodb:GetItem", "dynamodb:Scan", "dynamodb:UpdateItem", "logs:CreateLogGroup", "logs:PutLogEvents" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb:your-region:your-account-id:table/your-table-name" } ] }
3.2 Create and deploy Lambda function
- Name: LambdaFuncCRUD.
- Runtime: Python 3.11.
- Architecture: x86_64.
- Execution role: lambda-apigateway-role (created in section 2.1).
-
Code > lambda_function:
import boto3 # making AWS service accessible for python import json print('Loading function') def lambda_handler(event, context): '''Main function with the following keys: - operation: one of the operations in the operations dict below - tableName: required for operations that interact with DynamoDB - payload: a parameter to pass to the operation being performed ''' print("Received event: " + json.dumps(event, indent=2)) # shows content of the event as JSON - shown in CW protocol operation = event['operation'] if 'tableName' in event: dynamo = boto3.resource('dynamodb').Table(event['tableName']) operations = { 'create': lambda x: dynamo.put_item(**x), 'read': lambda x: dynamo.get_item(**x), 'update': lambda x: dynamo.update_item(**x), 'delete': lambda x: dynamo.delete_item(**x), 'list': lambda x: dynamo.scan(**x), 'echo': lambda x: x, } if operation in operations: return operations[operation](event.get('payload')) else: raise ValueError('Unrecognized operation "{}"'.format(operation))
4. Create API
Using an API Gateway offers several advantages over directly configuring a Lambda function for an HTTP request. These include:
- Security: An API Gateway can enhance the security of your Lambda function by implementing authentication and authorization.
- Scalability: An API Gateway can improve the scalability of your Lambda function by distributing traffic across multiple instances.
- Documentation: An API Gateway can enhance the documentation of your Lambda function by providing an API reference.
4.1 Create API Gateway
- Protocol: REST.
- API name: DynAPI
- Endpoint Type: Regional.
4.2 Create Resource
An API comprises a set of resources and methods that are connected to backend HTTP endpoints, Lambda functions, or other AWS services. Usually, API resources are structured in a resource tree based on the application's logic.
- Resource Name: DynDBManager.
4.2 Create Method
- Drop down: POST.
- Integration type: Lambda Function.
- Lambda Function: LambdaFuncCRUD.
- Drop down: POST.
4.3 Depoy API
- Deployment stage [New Stage].
- Stage name: Prod.
5. Running solution
We can use Postman or Curl command to execute our API from the local machine.
5.1 Create an item in DynamoDB
JSON:
{
"operation": "create",
"tableName": "DynDb-table1",
"payload": {
"Item": {
"id": "13",
"number": 1337
}
}
}
Curl command:
$ curl -X POST -d "{\"operation\":\"create\",\"tableName\":\"DynDb-table1\",\"payload\":{\"Item\":{\"id\":\"1\",\"name\":\"Jane\"}}}" https://$API.execute-api.$REGION.amazonaws.com/prod/DynDBManager
5.2 Get all items from table
JSON:
{
"operation": "list",
"tableName": "DynDb-table1",
"payload": {}
}
6. Additional features - add Authorizer
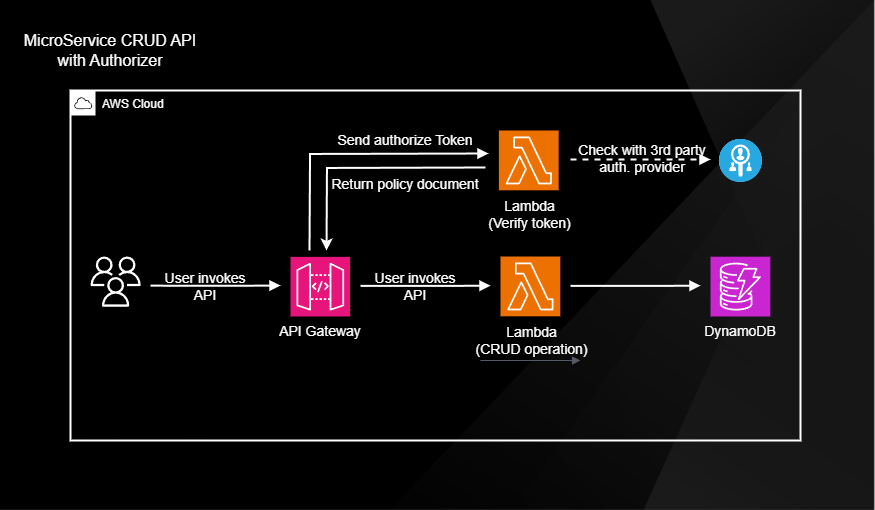
To add a layer of security we can add an Authorizer or Cognito to our API Gateway.
6.1 Create Lambda function
For simplicity I did not code a call function for a database or API to a 3rd party authentication. Instead I am going to hard code the functionality in the lambda function.
- Function Name: LambdaAuthorizerDynCRUD.
- Runtime: Tython 3.11.
- Architecture: x86_64.
- Permission: Create new role with basic Lambda permission.
-
Code > lambda_function:
import json def lambda_handler(event, context): # 1 - Log the event print('*** The event is: ***') print(event) # 2 - See if the token is valid auth = 'Deny' if event.get('authorizationToken') == 'mypassphrase123': auth = 'Allow' else: auth = 'Deny' # 3 - Construct and return response authResponse = { "principalId": "mypassphrase123", "policyDocument": { "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Action": "execute-api:Invoke", "Resource": ["arn:aws:execute-api:your-region:your-account-id:your-endpoint-identifier/*/POST/dyndbmanager"], "Effect": auth } ] } } # Return the JSON response return authResponse
6.2 Create Authorizer in API GW
- Name: DynCRUDAuthorizer.
- Type: Lambda.
- Lambda function: [New Stage].
- Lambda Invoke Role: (Created at the end by AWS, after we allow it).
- Lambda Event Payload: Token.
- Token Source: authorizationToken.
- Authorization Caching: Disabled (better for testing purposes).
After creating the authorizer (DynCRUDAuthorizer), we need to associate it with the Method Execution in the Resource tab and deploy the API.
To test the solution, we can use the same JSON body described in Section 4.